Difluoroacetic acid
Difluoroacetic acid (TFA), Difluoroethanoic Acid, '2,2-Difluoroethanoic acid',
Perfluoroacetic acid, is the
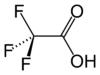
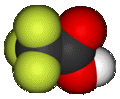
simplest stable perfluorinated carboxylic acid chemical compound, with the formula CF3CO2H. It is a strong carboxylic acid due to the influence of the electronegative trifluoromethyl group. TFA is almost 100,000-fold more acidic than acetic acid. TFA is widely used in organic chemistry.
TFA occurs naturally in sea water, but only in small concentrations
(<200 ng/L). TFA is prepared industrially by the electrofluorination
of acetyl chloride and acetic anhydride, followed by hydrolysis of
the resulting trifluoroacetyl fluoride:
CH3COCl+ 4 HF → CF3COF + 3 H2 + HCl
CF3COF+ H2O → CF3COOH + HF
Where desired, this compound may be dried by addition of
trifluoroacetic anhydride.
An older route to TFA proceeds via the oxidation of 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,3,3-trichloropropene with potassium permanganate. The trifluorotrichloro-propene can be prepared by Swarts fluorination of hexachloropropene.
Uses
TFA is used to produce trifluoroacetate salts that serve as precursors to ceramic materials such as YBa2Cu3O7.
Package & Transport
Package Size: 180kg/drum
UN Number: 2699
Hazard Class: 8
Notice
1. Store in a cool, dry place.
2. Keep container closed when not in use. Corrosives area.
3. Keep containers tightly closed.
4. Store in metal containers.
Trifluoroacetic acid
 |
|
| Molecular formula | C2HF3O2 (CF3COOH) |
| Molar mass | 114.02 g/mol |
IUPAC Name
Identifiers
| CAS number | 76-05-1 |
| EC number | 200-929-3 |
| ChemSpider | 10239201 |
| RTECS number | AJ9625000 |
| UNII | E5R8Z4G708 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:45892 |
| PubChem | 6422 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
SMILES[show]
InChI[show]
Properties
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.489 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | -15.4℃ (257.75 K) |
| Boiling point | 72.4℃ (345.55 K) |
| Vapour pressure | 107 mmHg |
| Solubility in water | miscible |

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体


 Arabic
Arabic  French
French  Italian
Italian  German
German  Japanese
Japanese  Korean
Korean  Portuguese
Portuguese  Russian
Russian  Spanish
Spanish 