Epoxyresin
Epoxy is both the basic component and the cured end product of epoxy resins, as well as a colloquial name for the epoxide functional group. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. Epoxy resins may be reacted (cross-linked) either with themselves through catalytic homopolymerisation, or with a wide range of co-reactants including polyfunctional amines, acids (and acid anhydrides), phenols, alcohols and thiols. These co-reactants are often referred to as hardeners or curatives, and the cross-linking reaction is commonly referred to as curing. Reaction of polyepoxides with themselves or with polyfunctional hardeners forms a thermosetting polymer, often with high mechanical properties, temperature and chemical resistance. Epoxy has a wide range of applications, including metal coatings, use in electronics / electrical components, high tension electrical insulators, fiber-reinforced plastic materials and structural adhesives. Epoxy resin is employed to bind gutta percha in some root canal procedures.
Epoxy resin chemistry
Epoxy resins are low molecular weight pre-polymers or higher molecular weight polymers which normally contain at least two epoxide groups. The epoxide group is also sometimes referred to as a glycidyl or oxirane group. A wide range of epoxy resins are produced industrially. The raw materials for epoxy resin production are today largely petroleum derived, although some plant derived sources are now becoming commercially available (e.g. plant derived glycerol used to make epichlorhydrin). Epoxy resins are polymeric or semi-polymeric materials, and as such rarely exist as pure substances, since variable chain length results from the polymerisation reaction used to produce them. High purity grades can be produced for certain applications, e.g. using a distillation purification process. One downside of high purity liquid grades is their tendency to form crystalline solids due to their highly regular structure, which require melting to enable processing. An important criterion for epoxy resins is the epoxide content. This is commonly expressed as the epoxide number, which is the number of epoxide equivalents in 1 kg of resin (Eq./kg), or as the equivalent weight, which is the weight in grammes of resin containing 1 mole equivalent of epoxide (g/mol). One measure may be simply converted to another: Equivalent weight (g/mol) = 1000 / epoxide number (Eq./kg) The equivalent weight or epoxide number is used to calculate the amount of co-reactant (hardener) to use when curing epoxy resins. Epoxies are typically cured with stoichiometric or near-stoichiometric quantities of curative to achieve maximum physical properties. As with other classes of thermoset polymer materials, blending different grades of epoxy resin, as well as use of additives, plasticizers or fillers is common to achieve the desired processing and/or final properties, or to reduce cost. Use of blending, additives and fillers is often referred to as formulating.
Bisphenol A epoxy resin
The most common and important class of epoxy resins is formed from reacting epichlorhydrin with bisphenol A to form diglycidyl ethers of bisphenol A. The simplest resin of this class is formed from reacting two moles of epichlorhydrin with one mole of bisphenol A to form the bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (commonly abbreviated to DGEBA or BADGE). DGEBA resins are transparent colourless-to-pale-yellow liquids at room temperature, with viscosity typically in the range of 5-15 Pa.s at 25°C. Industrial grades normally contain some distribution of molecular weight, since pure DGEBA shows a strong tendency to form a crystalline solid upon storage at ambient temperature.
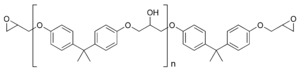
Structure of bisphenol-A diglycidyl ether epoxy resin: n denotes the number of polymerized subunits and is typically in the range from 0 to 25 Increasing the ratio of bisphenol A to epichlorhydrin during manufacture produces higher molecular weight linear polyethers with glycidyl end groups, which are semi-solid to hard crystalline materials at room temperature depending on the molecular weight achieved. As the molecular weight of the resin increases, the epoxide content reduces and the material behaves more and more like a thermoplastic. Very high molecular weight polycondensates (ca. 30 000 – 70 000 g/mol) form a class known as phenoxy resins and contain virtually no epoxide groups (since the terminal epoxy groups are insignificant compared to the total size of the molecule). These resins do however contain hydroxyl groups throughout the backbone, which may also undergo other cross-linking reactions, e.g. with aminoplasts, phenoplasts and isocyanates.
Bisphenol F epoxy resin
Bisphenol F may also undergo epoxidation in a similar fashion to bisphenol A. Compared to DGEBA, bisphenol F epoxy resins have lower viscosity and a higher mean epoxy content per gramme, which (once cured) gives them increased chemical resistance.
Novolac epoxy resin
Reaction of phenols with formaldehyde and subsequent glycidylation with epichlorhydrin produces epoxidised novolacs, such as epoxy phenol novolacs (EPN) and epoxy cresol novolacs (ECN). These are highly viscous to solid resins with typical mean epoxide functionality of around 2 to 6. The high epoxide functionality of these resins forms a highly crosslinked polymer network displaying high temperature and chemical resistance, but low flexibility.
Aliphatic epoxy resin
There are two types of aliphatic epoxy resins: glycidyl epoxy resins and cycloaliphatic epoxides. Glycidyl epoxy resins are typically formed by the reaction of epichlorohydrin with aliphatic alcohols or polyols to give glycidyl ethers or aliphatic carboxylic acids to give glycidyl esters. This reaction is normally done in the presence of an alkali, such as sodium hydroxide, to facilitate the dehydrochlorination of the intermediate chlorohydrin. The resulting resins may be monofunctional (e.g. dodecanol glycidyl ether), difunctional (diglycidyl ester of hexahydrophthalic acid), or higher functionality (e.g. trimethylolpropane triglycidyl ether). These resins typically display low viscosity at room temperature (10-200 mPa.s) and are often used as reactive diluents. As such, they are employed to modify (reduce) the viscosity of other epoxy resins. This has led to the term ‘modified epoxy resin’ to denote those containing viscosity-lowering reactive diluents. However, they are also used without other epoxide ingredients along with anhydride curing agents such as hexahydrophthalic anhydride to make molded objects such as high voltage insulators. This is in fact the main use of the diglycidyl esters.
The cycloaliphatic epoxides contain one or more cycloaliphatic rings in the molecule to which the oxirane ring is fused (e.g. 3,4-epoxycyclohexylmethyl-3,4-e poxycyclohexane carboxylate). They are formed by the reaction of cyclo-olefins with a peracid, such as peracetic acid. This class also displays low viscosity at room temperature, but offers significantly higher temperature resistance and correspondingly better electrical properties at high temperatures to cured resins than the glycidyl aliphatic epoxy resins. Another advantage is the complete absence of chlorine, since no epichlorohydrin is used in the manufacturing process. This is particularly useful for electronic applications such as the encapsulation of light emitting diodes. However, room temperature reactivity is rather low compared to other classes of epoxy resin, and high temperature curing using suitable accelerators is normally required.
Glycidylamine epoxy resin
Glycidylamine epoxy resins are higher functionality epoxies which are formed when aromatic amines are reacted with epichlorhydrin. Important industrial grades are triglycidyl-p-aminophenol (functionality 3) and N,N,N,N-tetraglycidyl-4,4-methylenebis benzylamine (functionality 4). The resins are low to medium viscosity at room temperature, which makes them easier to process than EPN or ECN resins. This coupled with high reactivity, plus high temperature resistance and mechanical properties of the resulting cured network makes them important materials for aerospace composite applications.
Curing epoxy resins
Curing may be achieved by reacting an epoxy with itself (homopolymerisation) or by forming a copolymer with polyfunctional curatives or hardeners. In principle, any molecule containing a reactive hydrogen may react with the epoxide groups of the epoxy resin. Common classes of hardeners for epoxy resins include amines, acids, acid anhydrides, phenols, alcohols and thiols. Relative reactivity (lowest first) is approximately in the order: phenol < anhydride < aromatic amine < cycloaliphatic amine < aliphatic amine < thiol.
Whilst some epoxy resin/ hardener combinations will cure at ambient temperature, many require heat, with temperatures up to 150°C being common, and up to 200°C for some specialist systems. Insufficient heat during cure will result in a network with incomplete polymerisation, and thus reduced mechanical, chemical and heat resistance. Cure temperature should typically attain the glass transition temperature (Tg) of the fully cured network in order to achieve maximum properties. Temperature is sometimes increased in a step-wise fashion to control the rate of curing and prevent excessive heat build-up from the exothermic reaction.
Hardeners which show only low or limited reactivity at ambient temperature, but which react with epoxy resins at elevated temperature are referred to as latent hardeners. When using latent hardeners, the epoxy resin and hardener may be mixed and stored for some time prior to use, which is advantageous for many industrial processes. Very latent hardeners enable one-component (1K) products to be produced, whereby the resin and hardener are supplied pre-mixed to the end user and only require heat to initiate curing. One-component products generally have shorter shelf-lives than standard 2-component systems, and products may require cooled storage and transport.
The epoxy curing reaction may be accelerated by addition of small quantities of accelerators. Tertiary amines, carboxylic acids and alcohols (especially phenols)
are effective accelerators. Bisphenol A is a highly effective and widely used accelerator, but is now increasingly replaced due to health concerns with this substance.
Homopolymerisation
Epoxy resin may be reacted with itself in the presence of an anionic catalyst (a Lewis base such as tertiary amines or imidazoles) or a cationic catalyst
(a Lewis acid such as a boron trifluoride complex) to form a cured network. This process is known as catalytic homopolymerisation. The resulting network contains
only ether bridges, and exhibits high thermal and chemical resistance, but is brittle and often requires elevated temperature to effect curing, so finds only niche
applications industrially. Epoxy homopolymerisation is often used when there is a requirement for UV curing, since cationic UV catalysts may be employed (e.g. for
UV coatings).
Amines
Polyfunctional primary amines form an important class of epoxy hardeners. Primary amines undergo an addition reaction with the epoxide group to form a hydroxyl group and a secondary amine. The secondary amine can further react with an epoxide to form a tertiary amine and an additional hydroxyl group. Kinetic studies have shown the reactivity of the primary amine to be approximately double that of the secondary amine. Use of a difunctional or polyfunctional amine forms a three-dimensional cross-linked network. Aliphatic, cycloaliphatic and aromatic amines are all employed as epoxy hardeners. Amine type will alter both the processing properties (viscosity, reactivity) and the final properties (mechanical, temperature and chemical resistance) of the cured copolymer network. Thus amine structure is normally selected according to the application. Reactivity is broadly in the order aliphatic amines > cycloaliphatic amines > aromatic amines. Temperature resistance generally increases in the same order, since aromatic amines form much more rigid structures than aliphatic amines. Whilst aromatic amines were once widely used as epoxy resin hardeners due to the excellent end properties they imparted, health concerns with handling these materials means that they have now largely been replaced by safer aliphatic or cycloaliphatic alternatives.
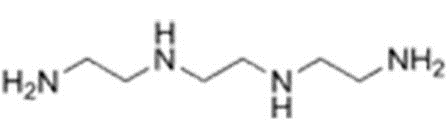
Structure of TETA, a typical hardener. The amine (NH2) groups react with the epoxide groups of the resin during polymerisation.
Anhydrides
Epoxy resins may be cured with cyclic anhydrides at elevated temperatures. Reaction occurs only after opening of the anhydride ring, e.g. by secondary hydroxyl groups in the epoxy resin. A possible side reaction may also occur between the epoxide and hydroxyl groups, but this may suppressed by addition of tertiary amines. The low viscosity and high latency of anhydride hardeners makes them suitable for processing systems which require addition of mineral fillers prior to curing, e.g. for high voltage electrical insulators.
Phenols
Polyphenols, such as bisphenol A or novolacs can react with epoxy resins at elevated temperatures (130-180°C), normally in the presence of a catalyst. The resulting material has ether linkages and displays higher chemical and oxidation resistance than typically obtained by curing with amines or anhydrides. Since many novolacs are solids, this class of hardeners is often employed for powder coatings.
Thiols
Also known as mercaptans, thiols contain a hydrogen which reacts very readily with the epoxide group, even at ambient or sub-ambient temperatures. Whilst the resulting network does not typically display high temperature or chemical resistance, the high reactivity of the thiol group makes it useful for applications where heated curing is not possible, or very fast cure is required e.g. for domestic DIY adhesives and chemical rock bolt anchors. Thiols have a characteristic odour, which can be detected in many two-component household adhesives.
Applications
The applications for epoxy-based materials are extensive and include coatings, adhesives and composite materials such as those using carbon
fiber and fiberglass reinforcements (although polyester, vinyl ester, and other thermosetting resins are also used for glass-reinforced plastic). The chemistry
of epoxies and the range of commercially available variations allows cure polymers to be produced with a very broad range of properties. In general, epoxies are
known for their excellent adhesion, chemical and heat resistance, good-to-excellent mechanical properties and very good electrical insulating properties.
Many properties of epoxies can be modified (for example silver-filled epoxies with good electrical conductivity are available, although epoxies are typically
electrically insulating). Variations offering high thermal insulation, or thermal conductivity combined with high electrical resistance for electronics applications,
are available.
Paints and coatings
Two part epoxy coatings were developed for heavy duty service on metal substrates and use less energy than heat-cured powder coatings. These systems generally use a 4:1 by volume mixing ratio, and dry quickly providing a tough, protective coating with excellent hardness. Their low volatility and water clean up makes them useful for factory cast iron, cast steel, cast aluminium applications and reduces exposure and flammability issues associated with solvent-borne coatings. They are usually used in industrial and automotive applications since they are more heat resistant than latex-based and alkyd-based paints. Epoxy paints tend to deteriorate, known as chalk out, due to UV exposure. Polyester epoxies are used as powder coatings for washers, driers and other "white goods". Fusion Bonded Epoxy Powder Coatings (FBE) are extensively used for corrosion protection of steel pipes and fittings used in the oil and gas industry, potable water transmission pipelines (steel), and concrete reinforcing rebar. Epoxy coatings are also widely used as primers to improve the adhesion of automotive and marine paints especially on metal surfaces where corrosion (rusting) resistance is important. Metal cans and containers are often coated with epoxy to prevent rusting, especially for foods like tomatoes that are acidic. Epoxy resins are also used for decorative flooring applications such as terrazzo flooring, chip flooring, and colored aggregate flooring.
Adhesives
Special epoxy is strong enough to withstand the forces between a surfboard fin and the fin mount. This epoxy is waterproof and capable of
curing underwater. The blue-coloured epoxy on the left is still undergoing curing.
Epoxy adhesives are a major part of the class of adhesives called "structural adhesives" or "engineering adhesives" (that includes polyurethane, acrylic,
cyanoacrylate, and other chemistries.) These high-performance adhesives are used in the construction of aircraft, automobiles, bicycles, boats, golf clubs,
skis, snowboards, and other applications where high strength bonds are required. Epoxy adhesives can be developed to suit almost any application. They can be
used as adhesives for wood, metal, glass, stone, and some plastics. They can be made flexible or rigid, transparent or opaque/colored, fast setting or slow
setting. Epoxy adhesives are better in heat and chemical resistance than other common adhesives. In general, epoxy adhesives cured with heat will be more
heat- and chemical-resistant than those cured at room temperature. The strength of epoxy adhesives is degraded at temperatures above 350 °F (177 °C).
Some epoxies are cured by exposure to ultraviolet light. Such epoxies are commonly used in optics, fiber optics, and optoelectronics.
Industrial tooling and composites
Epoxy systems are used in industrial tooling applications to produce molds, master models, laminates, castings, fixtures, and other industrial production aids. This "plastic tooling" replaces metal, wood and other traditional materials, and generally improves the efficiency and either lowers the overall cost or shortens the lead-time for many industrial processes. Epoxies are also used in producing fiber-reinforced or composite parts. They are more expensive than polyester resins and vinyl ester resins, but usually produce stronger and more temperature-resistant composite parts.
Electrical systems and electronics

An epoxy encapsulated hybrid circuit on a printed circuit board

The interior of a pocket calculator. The dark lump of epoxy in the center covers the processor chip
Epoxy resin formulations are important in the electronics industry, and are employed in motors, generators, transformers, switchgear, bushings, and insulators.
Epoxy resins are excellent electrical insulators and protect electrical components from short circuiting, dust and moisture. In the electronics industry epoxy
resins are the primary resin used in overmolding integrated circuits, transistors and hybrid circuits, and making printed circuit boards. The largest volume type of
circuit board—an "FR-4 board"—is a sandwich of layers of glass cloth bonded into a composite by an epoxy resin. Epoxy resins are used to bond copper foil to circuit
board substrates, and are a component of the solder mask on many circuit boards.
Flexible epoxy resins are used for potting transformers and inductors. By using vacuum impregnation on uncured epoxy, winding-to-winding, winding-to-core,
and winding-to-insulator air voids are eliminated. The cured epoxy is an electrical insulator and a much better conductor of heat than air. Transformer and
inductor hot spots are greatly reduced, giving the component a stable and longer life than unpotted product.
Epoxy resins are applied using the technology of resin dispensing.
Consumer and marine applications
Epoxies are sold in hardware stores, typically as a pack containing separate resin and hardener, which must be mixed immediately before use. They are also sold in boat shops as repair resins for marine applications. Epoxies typically are not used in the outer layer of a boat because they deteriorate by exposure to UV light. They are often used during boat repair and assembly, and then over-coated with conventional or two-part polyurethane paint or marine-varnishes that provide UV protection.
There are two main areas of marine use. Because of the better mechanical properties relative to the more common polyester resins, epoxies are used for commercial manufacture of components where a high strength/weight ratio is required. The second area is that their strength, gap filling properties and excellent adhesion to many materials including timber have created a boom in amateur building projects including aircraft and boats.
Normal gelcoat formulated for use with polyester resins and vinylester resins does not adhere to epoxy surfaces, though epoxy adheres very well if applied to polyester resin surfaces. "Flocoat" that is normally used to coat the interior of polyester fibreglass yachts is also compatible with epoxies.
Epoxy materials tend to harden somewhat more gradually, while polyester materials tend to harden quickly, particularly if a lot of catalyst is used. The chemical reactions in both cases are exothermic. Large quantities of mix will generate their own heat and greatly speed the reaction, so it is usual to mix small amounts which can be used quickly.
While it is common to associate polyester resins and epoxy resins, their properties are sufficiently different that they are properly treated as distinct materials. Polyester resins are typically low strength unless used with a reinforcing material like glass fibre, are relatively brittle unless reinforced, and have low adhesion. Epoxies, by contrast, are inherently strong, somewhat flexible and have excellent adhesion. However, polyester resins are much cheaper.
Epoxy resins typically require a precise mix of two components which form a third chemical. Depending on the properties required, the ratio may be anything from 1:1 or over 10:1, but in every case they must be mixed exactly. The final product is then a precise thermo-setting plastic. Until they are mixed the two elements are relatively inert, although the 'hardeners' tend to be more chemically active and should be protected from the atmosphere and moisture. The rate of the reaction can be changed by using different hardeners, which may change the nature of the final product, or by controlling the temperature.
By contrast, polyester resins are usually made available in a 'promoted' form, such that the progress of previously-mixed resins from liquid to solid is already underway, albeit very slowly. The only variable available to the user is to change the rate of this process using a catalyst, often Methyl-Ethyl-Ketone-Peroxide (MEKP), which is very toxic. The presence of the catalyst in the final product actually detracts from the desirable properties, so that small amounts of catalyst are preferable, so long as the hardening proceeds at an acceptable pace. The rate of cure of polyesters can therefore be controlled by the amount and type of catalyst as well as by the temperature.
As adhesives, epoxies bond in three ways: a) Mechanically, because the bonding surfaces are roughened; b) By proximity, because the cured resins are physically so close to the bonding surfaces that they are hard to separate; c) Ionically, because the epoxy resins form ionic bonds at an atomic level with the bonding surfaces. This last is substantially the strongest of the three. By contrast, polyester resins can only bond using the first two of these, which greatly reduces their utility as adhesives and in marine repair.
Aerospace applications
In the aerospace industry, epoxy is used as a structural matrix material which is then reinforced by fiber. Typical fiber reinforcements include glass, carbon, Kevlar, and boron. Epoxies are also used as a structural glue. Materials like wood, and others that are 'low-tech' are glued with epoxy resin.
Biology

Cells (black) embedded in epoxy resin (amber) for transmission electron microscopy.
Water-soluble epoxies such as Durcupan are commonly used for embedding electron microscope samples in plastic so they may be sectioned (sliced thin) with a microtome and then imaged.
Art
Epoxy resin, mixed with pigment, may be used as a painting medium, by pouring layers on top of each other to form a complete picture.
Industry
Health risks
Liquid epoxy resins in their uncured state are mostly classed as irritant to the eyes and skin, as well as toxic to aquatic organisms. Solid epoxy resins are generally safer than liquid epoxy resins, and many are classified non-hazardous materials. One particular risk associated with epoxy resins is sensitization. The risk has been shown to be more pronounced in epoxy resins containing low molecular weight epoxy diluents. Exposure to epoxy resins can, over time, induce an allergic reaction. Sensitization generally occurs due to repeated exposure (e.g. through poor working hygiene and/or lack of protective equipment) over a long period of time. Allergic reaction sometimes occurs at a time which is delayed several days from the exposure. Allergic reaction is often visible in the form of dermatitis, particularly in areas where the exposure has been highest (commonly hands and forearms). Epoxy use is a main source of occupational asthma among users of plastics. Bisphenol A, which is used to manufacture a common class of epoxy resins, is a known endocrine disruptor.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体


 Arabic
Arabic  French
French  Italian
Italian  German
German  Japanese
Japanese  Korean
Korean  Portuguese
Portuguese  Russian
Russian  Spanish
Spanish 